WHAT’S INSIDE:
A Quotation to Open On
Feature Article: Common Sense on Reliability Engineering (Part 2 of 3)
Systems Engineering News
- Artificial Intelligence for Engineering Design, Analysis and Manufacturing (AIEDAM) – Special Issue on Configuration
- ManTech to Offer Certifications from International Council on Systems Engineering
- Upcoming INCOSE Webinar on Architecting Resilient Systems
- INCOSE Election Results
- Invitation to SEMAT – The Software Engineering Method and Theory Initiative
- Applying Systems Thinking and Common Archetypes to Organizational Issues
Featured Societies – TBD
INCOSE Technical Operations – INCOSE Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS) Working Group
Systems Engineering Software Tools News
- Artisan Continues Industry Consolidation with Extessy Merger
- System Quality Requirements Engineering (SQUARE) Tool
- 3SL/Cradle: November 2009 Newsletter
Systems Engineering Books, Reports, Articles and Papers
- Errata
- Decision Making in Systems Engineering and Management
- Analytical Methods for Risk Management: A Systems Engineering Perspective
- Handbook of Research on Discrete Event Simulation Environments: Technologies and Applications
- Cause-Effect Diagrams: A Pragmatic Way of Doing Root-Cause Analysis
- UML Profiles Target DODAF, MODAF, SOA and Systems
- MV-22, F-35B: Systems Engineering Fail!
- Life Cycle of a Silver Bullet
- Behavioral Modeling for Embedded Systems and Technologies: Applications for Design and Implementation
- Call for Papers: ACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive Systems Special Issue On: Pervasive Adaptation: Visions & Challenges
- Human Factors in Requirements Engineering: – A Survey of Human Sciences Literature Relevant To the Improvement of Dependable Systems Development Processes
- Managing Legal Texts in Requirements Engineering
- Change Impact Analysis for SysML Requirements Models based on Semantics of Trace Relations
- Standard High Level Modelling Language Aids Safety Systems
- The Systems Engineering Delusion
Conferences and Meetings
Education and Academia
- Accelerated Master’s Program Aims to Provide Affordable Education, Career Training to Veterans in Only One Year
- New Certificate Programs Offered at Eastern Oregon University
Some Systems Engineering-Relevant Websites
Standards and Guides
- ISO/IEC/IEEE 12207 and 15288: The Entry-Level Standards for Process Definition – Part 1
A Definition to Close on – TBD
PPI News
PPI Events
A Quotation to Open On
TBD
Feature Article
Common Sense on Reliability Engineering – (Part 2 of 3)
Albertyn Barnard
Lambda Consulting
Pretoria, South Africa
ab@lambdaconsulting.co.za
“Unfortunately, the development of quality and reliability engineering has
been afflicted with more nonsense than any other branch of engineering.”
Patrick O’Connor
In the first part of this series, it was argued that Reliability is the absence of failures in products and systems. Furthermore, Reliability Engineering can be defined as the management function that prevents the creation of failures by people (such as systems engineers, design engineers, production personnel, users and maintenance personnel).
The ideal state of “absence of failures” can only be achieved in practice by preventing failures from occurring in the first place. However, the prevention of failure is only possible if we (preferably during design and development) develop a thorough understanding of potential failure modes, and then take appropriate steps to prevent them from occurring. This understanding of potential failure modes is obtained by using “Analysis” and “Test” as design and production verification methods as indicated in Figure 1.
Operations
Design verification (analysis
and test)
Design
Production verification (test)
Production
Figure 1: Verification of design and production
Reactive reliability (failure management)
Proactive reliability (failure prevention)
What is meant by “Analysis” in this context?
1 Design analysis
Many development activities involve both “design” and “analysis” aspects, which can be totally integrated or not, and which are typically iterative in nature. For example, an electronics engineer may select a certain circuit configuration, and then simulate (i.e. analyse) the chosen circuit to verify intended operation. In most cases, these circuit design tools can also be used to develop an understanding of potential product failure modes. In this example, the designer may include component tolerances, expected operating temperature and parameter drift with the nominal values in the simulation model and evaluate the design under worst case conditions (e.g. using Monte Carlo simulation).
Figure 2 shows the results of a worst case Monte Carlo simulation of an active low pass filter. If you intend to use this particular circuit in a product, variation in frequency response between individual products will most probably lead to unacceptable field reliability.
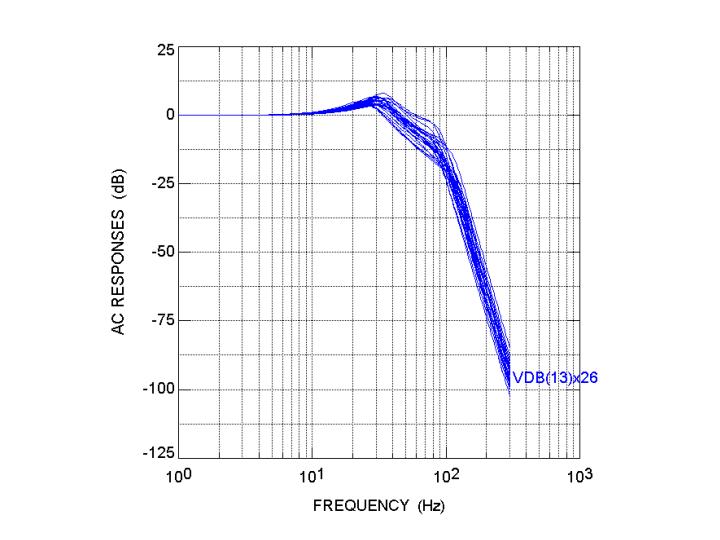
Figure 2 : Monte Carlo simulation of active low pass filter
There are many other examples of “design” tools that can be used as “analysis” tools. In fact, any design tool that provides knowledge on potential product failure modes, and the prevention thereof, can be used as valuable reliability engineering tool. Other examples include electronic component derating analysis, tolerance analysis, signal integrity analysis, electromagnetic compatibility analysis, thermal analysis, finite element analysis, vibration and shock analysis, load-strength analysis and fatigue analysis.
2 Failure analysis
Failure analysis, performed with the objective of understanding how the product or system will react to potential failure modes, is extremely useful to influence a design. Typical analyses include reliability block diagram analysis, design (and process) FMEA (Failure Mode and Effects Analysis) and FTA (Fault Tree Analysis).
FMEA can be described as a bottom-up analysis where potential failure modes of a product or system are identified, and the effects of these failure modes on a higher level are determined. For each potential failure mode, the probability of occurrence and the ability to detect it are also determined. FTA uses top-down logic to determine what failures (and in what combinations) can cause an undesirable event to occur. Both are well-known and very old reliability analysis tools. FMEA, for example, is described in US DoD standards dating from 1949.
FMEA is one of the most powerful reliability tools available, provided that it is used properly. It is therefore important to briefly highlight a major difference between a Design FMEA and a Logistics FMEA. Many engineers know that FMEA forms part of Logistic Support Analysis (LSA). Typically, in performing a LSA, the product or system Bill of Materials is used to develop a hardware breakdown structure, which forms the basis for listing failure modes. These failure modes are then used to identify logistic support in terms of spare parts, special test equipment and tools, maintenance personnel and documentation. The focus is on how to support the product or system when a failure has occurred. The focus of a design FMEA, on the other hand, is on how to prevent failure from occurring in the first place! It is much more than simply adding the word “failure” to a hardware item, and requires substantial technical input from design engineers. Many companies perform only logistics FMEA, and fail to reap the benefits of this powerful reliability analysis tool during development.
One of the fundamental weaknesses of FMEA results from asking the question “How can this item possibly fail?” Since this is a negative question, it may be difficult to identify all potential failure modes. A design engineer, in particular, may be reluctant to contribute to this process, since nobody is keen to publish a list of design weaknesses! An interesting approach to this problem is to change it into the positive question of “How can I change this design to cause a failure to happen?” In practice, this will immediately help to identify more failure modes, since every design engineer knows exactly how to change a configuration or a part or a parameter into a failure. This approach is known as Anticipatory Failure Determination®, and is an application of TRIZ (or Theory of the Solution of Inventive Problems) on FMEA [1].
Finally, it should be noted that reliability prediction (using the cancelled Mil-Hdbk-217) is not considered a useful reliability engineering analysis tool. This, and other similar reliability prediction methods which attempt to quantify reliability during development, are based on fundamentally flawed assumptions (e.g. Arrehenius equation). They have therefore limited (if any) ability to prevent failures from occurring in the field [2].
[The third and final part of this series will discuss “Test” as verification method in more detail with special reference to HALT and HASS – Editor].
References
http://www.ideationtriz.com
RWA Barnard, What is wrong with Reliability Engineering?, 18th Annual International Symposium of INCOSE, 15-19 June 2008, Utrecht, The Netherlands
biography
Albertyn Barnard received the degrees M Eng (Electronics) and M Eng (Engineering Management) from the University of Pretoria in South Africa. He has provided consulting services in reliability engineering to the defence, nuclear, aerospace and commercial industries since 1982. He provides training in reliability engineering to local industry and at post-graduate level at the University of Pretoria. He has presented numerous technical papers at local and international symposia, and won the Ad Sparrius Best Paper Award at the 2004 INCOSE SA conference, as well as the Gold Award at the 2009 International Applied Reliability Symposium Europe. He has been a member of the management committee of INCOSE SA for a number of years, and served as President of INCOSE SA in 2008. His company, Lambda Consulting, specialises in reliability engineering activities applicable to the development phase of products, with emphasis on reliability analysis of electronic design and HALT (Highly Accelerated Life Testing). Lambda Consulting established the first commercial HALT laboratory in South Africa in 2008.
Systems Engineering News
Artificial Intelligence for Engineering Design, Analysis and Manufacturing (AIEDAM) – Special Issue on Configuration
(Submission Deadline: March 20th 2010)
The goal of this special issue on configuration is to demonstrate novel and innovative configuration research as well as new industrial applications of configuration technologies. We encourage submissions describing novel results involving AI in configuration-related areas, including but not limited to:
- Theoretical issues justified by practical concerns;
- Methods for computing configurations and supporting configuration tasks;
- Methods for effective configuration knowledge base development, testing & debugging;
- Configuration and product/service/software design, product & service lifecycle management, and production management;
- Thorough case studies highlighting new practical problems, needs and experiences;
- Practical and new applications based on a well-defined theory or model.
Also welcome are articles that survey different approaches and thoroughly analyze their differences and commonalities.
ManTech to Offer Certifications from International Council on Systems Engineering
ManTech International Corporation (Nasdaq:MANT) and the International Council on Systems Engineering (INCOSE) announced that ManTech will offer INCOSE’s Certified Systems Engineering Professional (CSEP) program to its employees.
“ManTech is a leader in systems engineering and it is one of the most critical capabilities we provide our customers,” said Lawrence B. Prior, III, President and COO, ManTech International Corporation. “CSEP is a widely respected credential and our employees who achieve this certification will enhance their professional development and be able to use their increased skill and knowledge to benefit our customers.”
“INCOSE is pleased to enter this agreement with ManTech to advance the practice of systems engineering and to welcome their experts into our certification program. Together, we will build upon INCOSE’s CSEP designation as the worldwide reference for systems engineering professionalism,” said Pat Hale, President of INCOSE.
Upcoming INCOSE Webinar on Architecting Resilient Systems
Date: 16 Dec 2009
Time: 15:00 UTC
Presenter(s): Scott Jackson
General Webinar Details: http://www.incose.org/practice/webinars.aspx
INCOSE Election Results
INCOSE is pleased to announce the results of the recent elections and to congratulate the newly elected officers, directors and Member Board representatives.
New officers and directors will be inducted during the International Workshop in February, 2010.
President-Elect: John Thomas
Treasurer: Marsha Weiskopf
Director for Communications: Cecilia Haskins
Director for Strategy: Ralf Hartmann
Member Board Representatives:
- Region I: Robert Scheurer
- Region II: Eric Belle
- Region IV: Mike Dee
http://www.incose.org/newsevents/news/details.aspx?id=184
Invitation to SEMAT – The Software Engineering Method and Theory Initiative
By Ivar Jacobson, Bertrand Meyer, Richard Soley
You may have heard that the three of us have been quietly planning a “revolution”. The goal is to re-found software engineering as a rigorous discipline. We recognize that the natural tendency in our field is to perturb systems minimally into approximate correctness, but this path cannot be sustained any longer if we are to support the computing industry and help it meet the demands of society. We need to restart on a solid basis, taking advantage of all that has been learned in software engineering theory and practice over the past five decades.
Applying Systems Thinking and Common Archetypes to Organizational Issues
In this 40-minute web seminar, Michael Goodman will share his experience teaching and applying Systems Thinking in many Fortune 100-level businesses which helped guide development of the self-paced, online course, Applying Systems Thinking and Common Archetypes to Organizational Issues.
Presenter: Michael Goodman
Innovation Associates
Organizational Learning
Date: December 18, 2009
11:00 – 11:40 PM EST
Featured Society – TBD
TBD
More information
INCOSE Technical Operations
INCOSE Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS) Working Group
http://www.incose.org/practice/techactivities/wg/geoss/
Charter
Promote shared understanding and advancement of systems engineering practices and principles in the earth observation community.
Leadership Roles & Team Members
INCOSE Representative:
Lawrence McGovern, Northrop Grumman
Architecture and Data Committee Representative:
Lawrence McGovern, Northrop Grumman
User Interface Committee Representative:
Lawrence McGovern, Northrop Grumman
Team Members:
Elizabeth Davies, Northrop Grumman
Arthur J. Galloway, PhD, Consultant
For more information on GEOSS, visit the GEO website. Contact GEOSS Working Group for additional information or to join this group.
Accomplishments/Products
- Joined GEO as a participating organization in 2005.
- Have completed inputs to AIP1 and 2 and presented final report. See attached report.
- Presented Engineering Final Report for AIP 2 to 80 Ministry representatives from their respective countries in Melbourne, Australia in September 2009.
- Current tasking includes updates to nine Societal Based (SBA) Area View Scenario Viewpoints for Enterprise, Information and Computational views and building of Engineering and Technical Viewpoints for all Nine SBA Scenarios.
INCOSE currently participates on the Architecture and Data Committee and the User Interface Committee of GEOSS and is responsible for the UML Architecture development which was recently modified to include SysML syntax diagrams.
GEOSS Briefing to NDIA Conference on System Engineering – October 2009
![]() In Microsoft PowerPoint Size: 1.66MB
In Microsoft PowerPoint Size: 1.66MB
GEO Task List – November 2009
- Develop RMP-ODP UML Viewpoints for Engineering and Technical Viewpoints and update Enterprise, Information and Computational viewpoints for all nine SBAs.
- See Final Engineering Report for AIP2 (454kb)
Systems Engineering Software Tools News
Artisan Continues Industry Consolidation with Extessy Merger
Artisan Software Tools, has acquired Extessy, a supplier of development tools and services for system requirements, co-simulation, integration and test, based in Wolfsburg, Germany. Artisan’s acquisition of Extessy closely follows its acquisition last month of Brass Bullet, a leading UK systems engineering consultancy.
System Quality Requirements Engineering (SQUARE) Tool
A robust tool to support SQUARE has been developed by a team of Carnegie Mellon Master of Software Engineering students with oversight by Carnegie Mellon University staff within CERT, part of the Software Engineering Institute, and CyLab. The tool, designed for use by stakeholders, requirements engineers, and administrators, aids in all nine steps of SQUARE.
3SL/Cradle: November 2009 Newsletter
http://www.threesl.com/pages/webletter-November09/index.php
Systems Engineering Books, Reports, Articles and Papers
Errata
PPI apologises to the authors and to our readers for an error in SyEN#014 released on 25 November 2009.
The authors indicated for the following two books were swopped around by mistake. The correct information is:
Decision Making in Systems Engineering and Management
By Gregory S. Parnell, Patrick J. Driscoll, Dale L. Henderson
and
Analytical Methods for Risk Management: A Systems Engineering Perspective
By Paul R. Garvey
The complete references are re-printed below.
Decision Making in Systems Engineering and Management
By Gregory S. Parnell, Patrick J. Driscoll, Dale L. Henderson
Publisher’s Description: “This comprehensive textbook provides a logical process for fact-based decision making for the most challenging systems problems. It is composed of three bedrock elements to improve readers’ understanding and analysis of the most challenging systems problems that exist today: systems thinking, which identifies important interconnections between a system and its environment; systems engineering, which describes the activities of professional systems engineers; and systems decision making, which provides fact-based information to support major system decisions made at every life cycle stage.”
This hardcover book was published on February 8, 2008 in the Wiley Series in Systems Engineering and Management. ISBN-10: 0470165707, ISBN-13: 978-0470165706
Analytical Methods for Risk Management: A Systems Engineering Perspective
By Paul R. Garvey
Publisher’s Description: “A Text on the Foundation Processes, Analytical Principles, and Implementation Practices of Engineering Risk Management
Drawing from the author’s many years of hands-on experience in the field, the book presents the foundation processes and analytical practices for identifying, analyzing, measuring, and managing risk in traditional systems, systems-of-systems, and enterprise systems. After an introduction to engineering risk management, the book covers the fundamental axioms and properties of probability as well as key aspects of decision analysis, such as preference theory and risk/utility functions. It concludes with a series of essays on major analytical topics, including how to identify, write, and represent risks; prioritize risks in terms of their potential impacts on a systems project; and monitor progress when mitigating a risk’s potential adverse effects. The author also examines technical performance measures and how they can combine into an index to track an engineering system’s overall performance risk. In addition, he discusses risk management in the context of engineering complex, large-scale enterprise systems.
This hardcover book was published on October 20, 2008 by Chapman & Hall/CRC. ISBN-10: 1584886374, ISBN-13: 978-1584886372
Handbook of Research on Discrete Event Simulation Environments: Technologies and Applications
By Evon M. O. Abu-taieh, Asim Adbel Rahman El Sheikh
Publisher: Information Science Reference, Publication Date: 2009-10-20
ISBN-10 / ASIN: 1605667749, ISBN-13 / EAN: 9781605667744
 Product Description:
Product Description:
Discrete event simulation environments have desirable features and components now driving researchers to develop and enhance existing environments. The Handbook of Research on Discrete Event Simulation Environments: Technologies and Applications provides a comprehensive overview of theory and practice in simulation systems. A leading publication in this growing field, this Handbook of Research offers researchers, academicians, and practitioners progressive findings in simulation methodologies, modeling, standards, and applications.
Cause-Effect Diagrams: A Pragmatic Way of Doing Root-Cause Analysis
By Henrik Kniberg, Nov 16, 2009
Cause-effect diagrams are a simple and pragmatic way of doing root cause analysis. Henrik Kniberg shows you how cause-effect diagrams work, so you can put them to use in your own context.
UML Profiles Target DODAF, MODAF, SOA and Systems
The Unified Modeling Language (UML) has settled comfortably into its role of pulling together the technologies enterprises used to visually model software. UML has grown to comprise more than just software modeling diagrams. Profiles and specifications exist to expand its capabilities. The language has come to include 14 diagram types and a growing set of profiles.
MV-22, F-35B: Systems Engineering Fail!
There’s a new DARPA solicitation out that every MV-22 and JSF advocate must read.
Here’s the first paragraph:
“DARPA is soliciting innovative research proposals in the area of Thermal Management Systems (TMS) for aircraft landing decks. The deployment of the MV-22 Osprey has resulted in ship flight deck buckling that has been attributed to the excessive heat impact from engine exhaust plumes. Navy studies have indicated that repeated deck buckling will likely cause deck failure before planned ship life. With the upcoming deployment of the F-35B Short Take Off and Vertical Landing (STOVL) Joint Strike Fighter (JSF), it is anticipated that the engine exhaust plumes may have a more severe thermo-mechanical impact on the non-skid surface and flight deck structure of ships. Currently, there are no available strategies to mitigate deck buckling and thermal-mechanical deck failure other than heavy structural modifications. The goal of this effort is to exploit thermal management technologies that incorporate a thermally and functionally stable non-skid surface which meets Navy requirements for application, safety, and performance. Eligible technologies should consist of an integrated Thermal Management System (TMS) that mitigates the thermo-mechanical structural impact of the F-35B engine exhaust plumes. It is anticipated that the integrated TMS will be implemented on Navy Landing Helicopter Dock (LHD) 1 and Landing Helicopter Assault (LHA) 6 Class amphibious assault ships.”
Life Cycle of a Silver Bullet
Sarah A. Sheard, Software Productivity Consortium
“Attention! Throw out those other improvement methods – we have just discovered the best ever. With our method, your quality will go up and costs and cycle time will go down.” Almost any improvement method is hailed as the best way to save business from problems when it is new. Unfortunately, a few years later, this same method is now the reviled, flawed method that a new method is replacing. This parable tells how this happens.
Behavioral Modeling for Embedded Systems and Technologies: Applications for Design and Implementation
by Luís Gomes and João M. Fernandes
Publisher: Information Science Reference (July 16, 2009)
ISBN-10: 1605667501, ISBN-13: 978-1605667508
 Product Description:
Product Description:
The development of embedded systems offers a higher degree of abstraction, crucial to tackling the growing complexity and usage of model-driven approaches.
Behavioral Modeling for Embedded Systems and Technologies: Applications for Design and Implementation provides an overview of innovative behavior models currently used for developing embedded systems, accentuating graphical and visual notations. This dynamic compilation presents an authoritative reference collection to the most significant models of computation currently in use for embedded systems design.
Call for Papers: ACM Transactions on Autonomous and Adaptive Systems Special Issue on:
Pervasive Adaptation: Visions & Challenges
Pervasive Adaptation is concerned with models, tools, and technologies to be used in pervasive information and communication systems that are capable of autonomously adapting to highly dynamic contexts. The successful development of future pervasive systems will increasingly require handling complex interactions between intelligent objects, computers, sensors and actuators, and intelligent objects of any kind. The real challenge is to make such interactions fruitful, purposeful, and secure, despite the constantly changing characteristics of the environment (whether social, physical, or technical) in which such systems will operate, in the absence of any centralized control, and possibly even in the absence of a complete understanding of the structure and micro-level functioning of these systems. Clearly, the only way to approach this is to make systems able to adapt themselves (at the level of individual components or at the collective level) over situations and time, taking into account the overall emergent behavior of the system, and possibly offensively exploit the context dynamics to improve and evolve.
This special issues welcomes submissions on any topic related to pervasive adaptation. Survey/tutorial papers focusing on a specific topic of pervasive adaptation and aimed at framing the key concepts, challenges, and related work on that topic, are particularly welcome. Technical papers describing some original technical contribution are equally welcomed, provided they contain enough introductory/survey material to make the paper of general interest behind its specific technical contribution.
Human Factors in Requirements Engineering: – A Survey of Human Sciences Literature Relevant To the Improvement of Dependable Systems Development Processes
Authors: Stephan Viller, John Bowers, Tom Rodden
Abstract
Requirements engineering (RE) is an inherently social process, involving the contribution of individuals working in an organizational context. Further, failures in the RE process will potentially lead to systematic failures in the products that are produced as a result. Consequently, the RE process for dependable systems development should itself be considered as a dependable process, and therefore subject to greater scrutiny for vulnerabilities to error. Research on human error has typically focused on the work of individual actors from a cognitive perspective. This paper presents a survey which broadens the view on what contributes to human error by also examining work from the social and organizational literature. This review was conducted to inform efforts to improve the systems development process for dependable systems, and in particular their requirements engineering process.
Managing Legal Texts in Requirements Engineering
Authors: Paul N. Otto, Annie I. Antón
Abstract
Laws and regulations are playing an increasingly important role in requirements engineering and systems development. Monitoring systems for requirements and policy compliance has been recognized in the requirements engineering community as a key area for research. Similarly, legal compliance is critical in systems development, especially given that non-compliance can result in both financial and criminal penalties. Working with legal texts can be very challenging, however, because they contain numerous ambiguities, cross-references, domain-specific definitions, and acronyms, and are frequently amended via new statutes, regulations, and case law. Requirements engineers and compliance auditors must be able to identify relevant legal texts, extract requirements and other key concepts, and monitor compliance. This chapter surveys research efforts over the past 50 years in handling legal texts for systems development. This survey can aid requirements engineers and auditors to better specify, test, and monitor systems for compliance.
Change Impact Analysis for SysML Requirements Models based on Semantics of Trace Relations
Authors: ten Hove, D.; Göknil, A.; Kurtev, I.; van den Berg, K.G.; de Goede, K.
Editors Oldevik, J.; Olsen, G. K.; Neple, T.; Kolovos, D.
Summary
Change impact analysis is one of the applications of requirements traceability in software engineering community. In this paper, we focus on requirements and requirements relations from traceability perspective. We provide formal definitions of the requirements relations in SysML for change impact analysis. Our approach aims at keeping the model synchronized with what stakeholders want to be modeled, and possibly implemented as well, which we called as the domain. The differences between the domain and model are defined as external inconsistencies. The inconsistencies are propagated for the whole model by using the formalization of relations, and mapped to proposed model changes. We provide tool support which is a plug-in of the commercial visual software modeler BluePrint.
Standard High Level Modelling Language Aids Safety Systems
Matthew Hause looks at how a standard high level modelling language can help in the design and development of mission critical systems as they become standardised.
The Systems Engineering Delusion
“…The need for complex interaction between different specialists is not a new economic phenomenon, and in engineering it does indeed require project managers and technical directors who can take a multi-disciplinary overview. This, however, is quite distinct from the Systems Engineering ethos, which attempts to legitimise the creation of a separate discipline which specialises in the top-down analysis of engineering projects in terms of requirements, capabilities and stakeholders, abstracted from concrete engineering issues.”
Conferences and Meetings
Intermediate Dynamic Modeling with STELLA and iThink
Colorado Springs, CO — December 14-16, 2009
http://www.iseesystems.com/store/Training/InterDynamicModelingIthink.aspx
INCOSE 2010 International Workshop
February 07 – 10, 2010, Phoenix Marriott Mesa, Mesa, Arizona, USA
http://www.incose.org/newsevents/events/details.aspx?id=78
Semantic Models for Adaptive Interactive Systems
In conjunction with 2010 International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces (IUI 2010) in Hong Kong, China, on February 7th, 2010
1st Workshop on Semantically-Enabled Systems Engineering (SENSE-2010)
February, 15th – 18th 2010, Andrzej Frycz Modrzewski Cracow College, Krakow, Poland
http://www.ifs.tuwien.ac.at/SENSE-2010
IESS 1.0: First International Conference on Exploring Services Sciences
17-18-19 February 2010, Geneva, Switzerland
The 1st Workshop on Model Based Engineering for Embedded Systems Design
March 12, 2010 – Dresden, Germany
http://www.wikicfp.com/cfp/servlet/event.showcfp?eventid=6899©ownerid=3264
Aspect-Oriented Requirements Engineering and Architecture Design:
Early Aspects and Climate Change (Early Aspects at AOSD 2010)
15 March 2010
http://www.aosd-europe.net/eaAOSD2010
CSER 2010 8th Annual Conference on Systems Engineering Research
March 17-19, Hoboken, NJ, USA
http://sse.stevens.edu/research/sponsored-conferences/cser/2010/home/
![]() The 2010 International Symposium on Collaborative Technologies and Systems (CTS 2010)
The 2010 International Symposium on Collaborative Technologies and Systems (CTS 2010)
May 17-21, 2010, The Westin Lombard Yorktown Center, Chicago, Illinois, USA
http://cisedu.us/cis/cts/10/main/callForPapers.jsp
![]() Lean Software & Systems Conference 2010
Lean Software & Systems Conference 2010
April 21-23, 2010, Atlanta
http://www.devagile.com/modules/news/article.php?storyid=480
![]() 7th Workshop on System Testing and Validation (STV10)
7th Workshop on System Testing and Validation (STV10)
In conjunction with IEEE ECBS 2010, Oxford, UK
March 22-26, 2010
https://syst.eui.upm.es/conferences/stv10/
The Third Edition of the Requirements Engineering Track (RE-Track’10)
Part of the 25th ACM Symposium on Applied Computing. (SAC 2010)
22 – 26 March 2010, Sierre, Switzerland
http://www.dsc.upe.br/~sac2010/
Track on REAL-TIME SYSTEMS at ACM SAC 2010
21 – 26 March 2010, Sierre, Switzerland
http://cs.chaminade.edu/org/sac10
Quality of Model-Based Testing (QuoMBaT 2010)
![]() Paris, France
Paris, France
April 10, 2010
http://www.model-based-testing.de/quombat10/importantDates.html
CHI 2010 (ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems)
![]() 10 – 15 April 2010, Atlanta, GA, USA
10 – 15 April 2010, Atlanta, GA, USA
![]() 5th International Workshop on Model-Driven Development of Advanced User Experience and UI Engineering
5th International Workshop on Model-Driven Development of Advanced User Experience and UI Engineering
Organised at CHI 2010
10 – 15 April 2010, Atlanta, GA, USA
http://www.lero.ie/mddaui2010/
Symposium on Theory of Modeling and Simulation – DEVS Integrative M&S Symposium (DEVS’10)
April 11 – 15, as part of the 2010 Spring Simulation Multiconference at the Florida Mall Hotel and Conference Center in Orlando, FL, USA
WER’10: 13th Workshop on Requirements Engineering
April 12-13, 2010 – Cuenca, Ecuador
Agent-Directed Simulation Symposium (ADS’10)
Part of the 2010 Spring Simulation Multiconference (SpringSim’10)
April 12-15, 2010, Orlando, Florida, USA
http://www.site.uottawa.ca/~oren/conf-org/ADS_2010/ADS-CFP.htm
Second NASA Formal Methods Symposium (NFM 2010)
April 13 – 15, 2010, USA
http://shemesh.larc.nasa.gov/NFM2010/
COFES: Congress on the Future of Engineering Software (COFES) 2010
April 15-18, 2010, Scottsdale, Arizona, USA – The Scottsdale Plaza Resort
http://cofes.com/Home/tabid/36/Default.aspx
2010 The 2nd IEEE International Conference on Systems Engineering and Modeling (ICSEM 2010)
23 to 25 April 2010, Bangkok, Thailand
http://www.conferencealerts.com/seeconf.mv?q=ca1m6a3i
Systems Engineering and Test & Evaluation (SETE) 2010
3-6 May, 2010, Stamford Grand, Adelaide, Australia
http://www.sapmea.asn.au/conventions/sete2010/index.html
Software Process Improvement and Capability dEtermination (SPICE) 2010
18-20 May 2010 – Pisa, Italy
http://www.spiceconference.com/
EuSEC 2010: Systems Engineering and Innovation
23-26 May, 2010, Stockholm, Sweden
http://www.incose.org/eusec2010
The 22nd International Conference on Advanced Information Systems Engineering (CAiSE’10)
07-11 June 2010, Hammamet, Tunisia
21st IEEE International Symposium on Rapid System Prototyping
June 8-11, 2010, George Mason University, Fairfax, Virginia, USA
PETRI NETS 2010
June 21-25, 2010, Braga, Portugal
http://acsd-petrinets2010.di.uminho.pt/?page=PetriNets2010
ACSD 2010: 10th International Conference on Application of Concurrency to System Design
Collocated with Petri Nets 2010
June 21-25, 2010, Braga, Portugal
http://acsd-petrinets2010.di.uminho.pt/?page=ACSD2010
ISARCS 2010 – 1st International Symposium on Architecting Critical Systems
Federated with CompArch 2010
June 23-25 2010 Prague, Czech Republic
http://www.isarcs.org/isarcs2010/
![]() 16th International Working Conference on Requirements Engineering: Foundation for Software Quality (RefsQ 2010)
16th International Working Conference on Requirements Engineering: Foundation for Software Quality (RefsQ 2010)
30 June – 2 July, 2010, Essen, Germany
http://www.sse.uni-due.de/refsq/2010/
20th Annual INCOSE International Symposium
July 11 – 15, 2010, Hyatt Regency O’Hare, Rosemont, IL, USA
http://www.incose.org/newsevents/events/details.aspx?id=77
![]() 2nd International Workshop on Model-Driven User-Centric Design & Engineering (MDUCDE’10)
2nd International Workshop on Model-Driven User-Centric Design & Engineering (MDUCDE’10)
September 1st & 2nd, 2010, Valenciennes/France
http://www.zmmi.de/MDUCDE2010/
European Systems & Software Process Improvement and Innovation
![]() 1-3 September 2010, Grenoble Institute of Technology, France
1-3 September 2010, Grenoble Institute of Technology, France
The 18th International Requirements Engineering Conference (RE 2010)
Sep 27, 2010 – Oct 1, 2010, Sydney, Australia
http://www.wikicfp.com/cfp/servlet/event.showcfp?eventid=6800©ownerid=6809
![]() Fifth International Conference on Graph Transformation
Fifth International Conference on Graph Transformation
University Of Twente, Enschede, The Netherlands
27 September – 2 October, 2010
http://www.utwente.nl/icgt2010/
Fourth Asia-Pacific Conference on Systems Engineering (APCOSE 2010)
Keelung, Taiwan, October 4-6, 2010
http://www.incose-taiwanchapter.org/APCOSE2010/
![]() Sixth Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interaction (NordiCHI 2010)
Sixth Nordic Conference on Human-Computer Interaction (NordiCHI 2010)
October 16 – 20, Reykjavik Iceland
http://www.yourhost.is/nordichi2010
Complex Systems Design & Management 2010
October 27-29, 2010, Paris, France
http://www.incose-taiwanchapter.org/APCOSE2010/
![]() 2010 IITA International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems Engineering (CASE 2010)
2010 IITA International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems Engineering (CASE 2010)
Nov 7, 2010 – Nov 8, 2010
Taipei, Taiwan
http://www.wikicfp.com/cfp/servlet/event.showcfp?eventid=7428©ownerid=2
![]() ICECSE 2011 “International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Systems Engineering”
ICECSE 2011 “International Conference on Electrical, Computer and Systems Engineering”
January 25-27, 2011, Dubai, United Arab Emirates
http://www.waset.org/conferences/2011/dubai/icecse/
Education and Academia
Accelerated Master’s Program Aims to Provide Affordable Education, Career Training to Veterans in Only One Year
Tom Christensen, Cavalier Daily Associate Editor
The University of Virginia’s Department of Systems and Information Engineering has developed an Accelerated Master’s Program in systems engineering designed specifically for providing United States Veterans with inexpensive career and educational training.
New Certificate Programs Offered at Eastern Oregon University
Eastern Oregon University is hoping to open the door to high-demand careers in computer programming, web design and health care through a series of new certificate programs available beginning winter term………
Certificates in Computer Programming, Web Development, Systems Engineering, Intermediate Computer Programming and Spanish for Healthcare Professionals are the outcome of those meetings.
Some Systems Engineering-Relevant Websites
TBD
Standards and Guides
ISO/IEC/IEEE 12207 and 15288: The Entry-Level Standards for Process Definition – Part 1
James W. Moore
In 2008, the 12207 standard for software life cycle processes and the 15288 standard for system life cycle processes were revised in an effort that finally harmonized system and software processes as well as bringing the respective IEEE and ISO/IEC standards into complete agreement. Some users mistakenly believe that these standards are targeted only to large organizations able to make a substantial investment in a complete suite of software and systems processes. However, these standards are also the best entry point for beginning users who desire guidance on as few as a single process. This three-part article will explain how entry-level users can apply the two standards.
A Definition to Close on
TBD
PPI News
TBD
TBD
PPI Events (see www.ppi-int.com)
Systems Engineering Public 5-Day Courses (2009-2010)
{Julie to plug in list by location to end of December 2010}
Requirements Analysis and Specification Writing Public Courses (2009-2010)
{ Julie to plug in list by location to end of December 2010 }
Software Engineering Public 5-Day Courses (2009-2010)
{ Julie to plug in list by location to end of December 2010 }
OCD/CONOPS Public Courses (2009-2010)
{ Julie to plug in list by location to end of December 2010 }
Cognitive Systems Engineering Courses (2009-2010)
{ Julie to plug in list by location to end of December 2010 }
PPI Upcoming Participation in Professional Conferences
{Julie to plug in – cover the rest of 2009 and to July 2010}
Kind regards from the SyEN team:
Robert Halligan, Managing Editor, email: rhalligan@ppi-int.com
Alwyn Smit, Editor, email: asmit@ppi-int.com
Luke Simpson, Production, email: lsimpson@ppi-int.com
Project Performance International
2 Parkgate Drive, Ringwood, Vic 3004 Australia
Tel: +61 3 9876 7345
Fax: +61 3 9876 2664
Tel Brasil:
Tel UK:
Tel USA:
Web: www.ppi-int.com
Email: contact@ppi-int.com
Copyright 2009 Project Performance (Australia) Pty Ltd, trading as Project Performance International
Tell us what you think of SyEN: email to contact@ppi-int.com
If you do not wish to receive a copy monthly of SyEN in future, please reply to this e-mail with “Remove” in the subject line. All removals are acknowledged; you may wish to contact PPI if acknowledgement is not received within 7 days.