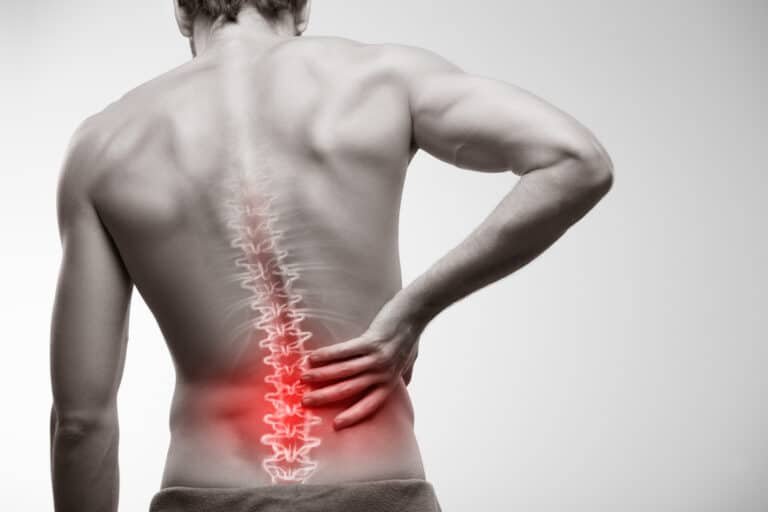
Innovative research at The Ohio State University has unveiled a new gene therapy using nanocarriers that could potentially replace opioids for back pain management. This gene therapy, explored in a study published in the journal Biomaterials, leverages nanocarriers derived from mouse connective tissue cells to deliver DNA that promotes tissue regeneration in spinal discs.
The study demonstrated that injecting these nanocarriers into mice with spinal injuries not only repaired the damaged discs but also significantly alleviated pain. The therapy focuses on the regeneration of spinal tissue and reduction of pain symptoms, showing promise as an effective treatment that could also improve surgical outcomes.
The nanocarriers are engineered to deliver a specific protein crucial for tissue development. This approach mimics the natural recovery processes, potentially reverting tissues back to a more youthful and functional state. The success of the therapy in mice has set the stage for further studies in older animal models, with the long-term to advance to clinical trials.
This method presents a sustainable alternative to opioids, aiming to address the root causes of back pain rather than merely managing symptoms. It reflects a significant step forward in the development of medical treatments that enhance the body’s natural healing processes and could revolutionize the way back pain and spinal injuries are treated in the future.
Adding to the complexity of the study, the researchers employed a multifaceted approach to assess the outcomes over a period of 12 weeks. Through imaging, tissue analysis, and mechanical and behavioral tests, they observed that gene therapy restored structural integrity and function to the degenerated discs and diminished signs of pain in the animals, highlighting the therapy’s dual benefits of regeneration and pain relief. This holistic evaluation underscores the potential of the therapy to bring significant improvements in the quality of life for patients suffering from disc-related ailments.
References
Greenwood, Matthew 2023, ‘Toyota’s new GenAI Tool is Transforming Vehicle Design’, Engineering.com, viewed 27th November 2023, <https://www.engineering.com/story/toyotas-new-genai-tool-is-transforming-vehicle-design>
Tang, Shirley N., Salazar-Puerta, Ana I., Heimann, Mary K., Kuchynsky, Kyle, Rincon-Benavides, María A., Kordowski, Mia, Gunsch, Gilian, Bodine, Lucy, Diop, Khady, Gantt, Connor, Khan, Safdar, Bratasz, Anna, Kokiko-Cochran, Olga, Fitzgerald, Julie, Laudier, Damien M., Hoyland, Judith A., Walter, Benjamin A., Higuita-Castro, Natalia, & Purmessur, Devina 2024, ‘Engineered extracellular vesicle-based gene therapy for the treatment of discogenic back pain’, ScienceDirect, viewed 28th May 2024, <https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142961224000966?via%3Dihub>